LED chip procurement: How to achieve both high brightness and low heat generation
- author:
- 2024-06-07 13:27:06
In the LED industry, the performance and quality of LED chips are crucial. In order to ensure that LED chips can perform their best results, we need to have an in-depth understanding and strict control of them. The following will explain in detail important contents about the light and heat distribution of LED chips.
- The light and heat distribution of the LED chip must be uniform, and there must be no case that the microscopic areas are too dark or overheated. When the microscopic photothermal distribution system is used to observe that the microscopic area of the chip is too dark and overheated, it is highly likely that there is current congestion here, resulting in excessive conversion of electrical energy into heat rather than light energy, and low quantum efficiency. This shows that there is room for improvement in the design of the chip.
- A microscopic photothermal distribution system needs to be used to compare the brightness value and heat value of the chip at the use temperature. The photothermal performance of LED light sources is greatly affected by temperature. When the temperature rises, the brightness of the chip decreases and the heat generation increases. Therefore, tests conducted outside the actual working temperature have poor accuracy and may even be meaningless.
- It is recommended to add light and heat distribution data at different operating temperatures to the LED specifications of the chip factory! Controlling quality from the source and inspecting incoming materials for light and heat distribution can make the LEDs reach the brightest and lowest temperature state, with the lowest cost and more reliable quality.
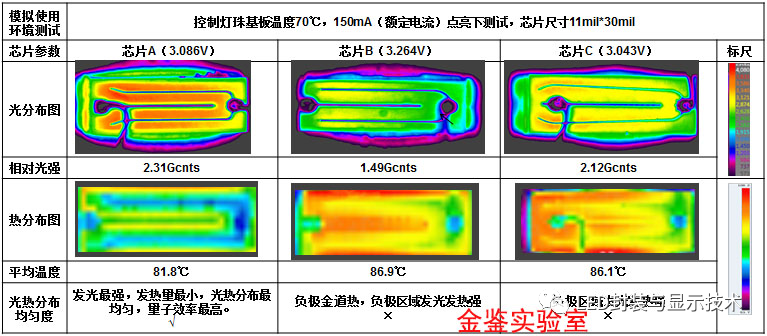
那么,为何来料 LED 芯片一定要进行光热分布测试呢?
- In the most commonly used horizontal structure chips on the market currently, the ohmic contact electrodes are located on the same side of the chip. Current inevitably has to be transmitted horizontally, and the current density will change with the distance between the electrodes, that is, in the areas close to the positive and negative electrodes, the current density will be large, resulting in uneven current density becoming an inherent technical bottleneck for horizontal structure LEDs.
- Many key technical issues related to the manufacturing of LED chips have not yet been completely resolved, especially the design of high-power LED chips, material selection in the manufacturing process, and process parameters, which make there is a large room for optimization for current density uniformity. Each chip (whether it is a horizontal structure or a vertical structure) will have large differences in current density uniformity.
- The current concentration effect generated inside the chip will cause undesirable phenomena such as reduced electric injection efficiency of the LED chip, uneven light emission, and local heat concentration, which in turn affects the performance and reliability of the LED chip.
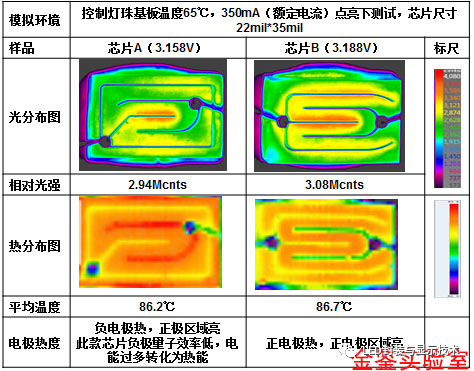
Case Study (2) Some chips have the positive electrode hotter, and some chips have the negative electrode hotter!
The following is a comparison of the light and heat distribution of chips with 22mil*35mil size from two manufacturers. For a high-power build-up chip of this size, the path for current to expand laterally in the chip is long, which leads to a more obvious current concentration effect. Therefore, reasonable electrode pattern design and good ohmic contact characteristics must be provided to ensure that the injected current is evenly distributed in the active layer of the LED chip. At present, many key technical issues related to the manufacturing of high-power LED chips have yet to be solved. The ability of each chip manufacturer to solve the problem is high or low, resulting in huge differences in the performance of different chips! It can be seen from the comparison of the light and heat distribution of the following two chips of the same size:
1. Compared with the 11*30mil chip, the current density uniformity of this large size and high power chip is relatively poor, which is also one of the technical bottlenecks in the development of high-power horizontal structure LED chips.
2. Through a large number of tests, it was found that different chips have different temperatures of the positive and negative electrodes. Some chips have hotter positive electrodes, and some chips have hotter negative electrodes, as shown in the following figure. Overheating of the electrode will cause the electrode metal to melt, degrade the ohmic contact characteristics, and reduce chip performance and reliability. People don't pay much attention to the heat of the electrodes. Perhaps the chip factory has not done such detailed research.
3. In this case, chip A has a strange phenomenon: the negative electrode is hotter, but the light is not strong, while the positive electrode area is brighter, but the temperature is not high. This shows that the quantum efficiency near the negative electrode of this chip is low, too much electrical energy is converted into heat energy there, and the ohmic contact reliability of the negative electrode is weak.
At present, most people pay attention to the overall performance of the LED chip, such as brightness, junction temperature, and voltage. They pay too little attention to the chip's light and heat distribution, current density distribution, etc., and failures often start from local weaknesses. It is strongly recommended that LED chip specifications add light and heat distribution data at different usage temperatures! Doing a good job in inspecting the light and heat distribution incoming materials can make the LEDs brightest, the lowest temperature, the lowest cost, and the more reliable quality.
通过以上对 LED 芯片光热分布及相关问题的深入探讨,我们清晰地认识到光热分布测试对于来料 LED 芯片的重要性。Only by strictly controlling this link and continuously optimizing the performance and quality of chips can we promote the sustained and healthy development of the LED industry and bring a more high-quality, efficient and reliable lighting experience to our lives. Let us pay attention to and attach importance to the light and heat distribution of LED chips and contribute to the progress of the industry.
TAG: