Analysis of Micro LED light-emitting chips with different structures
- author:
- 2024-06-07 13:46:41
At a time when display technology continues to develop, Micro LED display technology has gradually entered people's vision with its unique advantages. As a further evolution of traditional LED displays, it achieves micro-spacing and high-definition, showing huge application potential. One of the key elements is the LED chip, whose structure and packaging method have a crucial impact on the performance of Micro LED display devices.
Micro LED displays use tiny LED crystal particles as pixel light-emitting points. The LED chip structure and packaging method directly affect the performance of Micro LED display devices. An LED chip is usually composed of a substrate, a P-type semiconductor layer, an N-type semiconductor layer, a P-N junction and positive and negative electrodes. When a forward voltage is applied between the positive and negative electrodes, the holes injected from the P region to the N region and the electrons injected from the N region into the P region are recombined at the P-N junction, and electrical energy is converted into light energy, emitting light of different wavelengths.
01Micro LED chip type
There are three main structures of LED chips: formal structure, flip-chip structure and vertical structure.
Analysis of Micro LED light-emitting chips with different structures
02 Formal chip structure
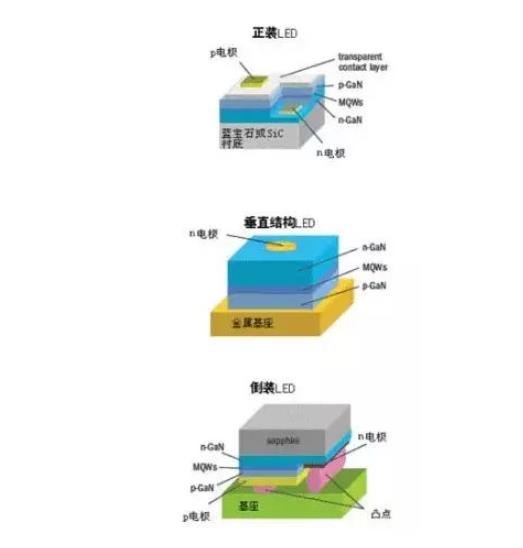
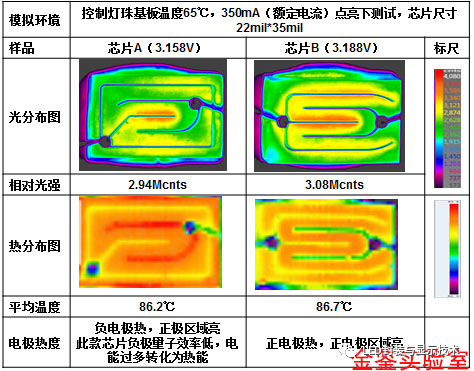
The formal chip is the earliest chip structure that appears. From top to bottom, the structure is: electrode, P-type semiconductor layer, light-emitting layer, N-type semiconductor layer and substrate. In this structure, the heat generated at the PN junction needs to pass through the sapphire substrate to be conducted to the heat sink. However, the poor thermal conductivity of the sapphire substrate leads to poor thermal conductivity of the structure, which in turn reduces the luminescent efficiency and reliability of the chip. In addition, in the formal chip structure, both the p electrode and the n electrode are located on the light emitting surface of the chip, and the blocking of the electrode will obviously affect the light emitting surface of the chip, resulting in low light emitting efficiency of the chip. At the same time, the positive and negative electrodes are located on the same side of the chip and are prone to current congestion, which will also reduce the luminous efficiency. In addition, factors such as temperature and humidity may cause electrode metal migration. As the chip size continues to shrink, the distance between positive and negative electrodes decreases, and electrode migration may cause short circuit problems.
03 Flip-chip structure
The flip chip structure is composed of a sapphire substrate, an N-type semiconductor layer, a light-emitting layer, a P-type semiconductor layer and an electrode from top to bottom. Compared with the formal structure, the heat generated at the PN junction in this structure can be directly conducted to the heat sink without passing through the substrate, so the heat dissipation performance is good, which makes the chip's luminous efficiency and reliability higher. In addition, in the flip chip structure, both the p electrode and the n electrode are on the bottom surface, which effectively avoids blocking the outgoing light, thereby improving the light emitting efficiency of the chip. Moreover, the distance between flip chip electrodes is long, which can reduce the risk of short circuit caused by electrode metal migration.
04 Vertical structure chip
Compared with formal chips, vertical structure chips use substrates with high thermal conductivity (substrates such as Si, Ge and Cu) to replace the sapphire substrate, which greatly improves the heat dissipation performance of the chip. At the same time, the positive and negative electrodes of the vertically structured chip are located on the upper and lower sides of the chip respectively, making the current distribution more uniform, avoiding the occurrence of local high temperatures and further improving the reliability of the chip. However, vertical chips currently face the problems of high cost and low mass production capacity.
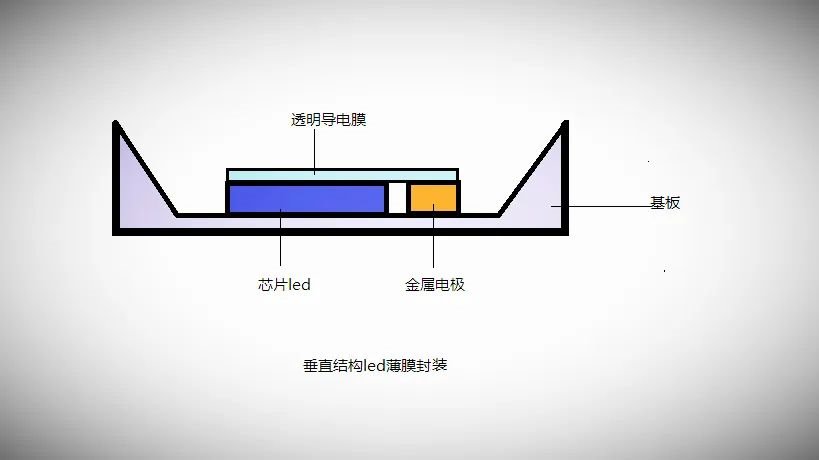
In short, Micro LED light-emitting chips with different structures have their own characteristics and advantages, and also face different challenges. With the continuous advancement and development of technology, I believe that these problems will be gradually solved, and Micro LED display technology will show broader application prospects in the future.
TAG: