LED display: type, design characteristics, how to choose an LED display
- author:
- 2024-09-03 16:27:48
LED screens are devices composed of many light emitting diodes (LEDs) that form an image.
In March 1978, the first sample of the screen was shown to the public in the United States as part of a science and technology exhibition. The author of the invention is James Mitchell. LED models can also operate at lower voltage levels, giving them a high degree of mobility and battery power capabilities. In the 21st century, there was a technological breakthrough, and the screen size was significantly reduced to the size of a TV. New oled technology based on organic elements makes this possible.
The screen is the first visual display device to provide a better user experience. They outperform other technologies in terms of image quality at any time of the day and flexible broadcast settings. The ability to create displays with any geometry also makes screens a leader among similar tools for displaying information to potential audiences. 
Working principle of LED screen
The operating principle of LED LED models is similar to that of a TV or computer monitor. The image is formed from three primary colors: red, green and blue. The abbreviation for this technology is RGB. A full-color image is obtained by combining light of different brightness from these three basic elements. High image resolution ensures the virtuality of pixels-each color of LED diodes can be combined in multiple ways with other diodes to form individual pixels.
Design, device and type of LED display
The design of the LED display consists of separate modules. LEDs can be combined into a matrix or cluster and connected to the image control section on the back of the device. Individual modules or LED boxes can operate independently of each other, allowing you to create a variety of configurations, including non-standard shapes. Such displays can be rectangular, square or assembled into convex or curved structures following the shape of their mounting surface. The main operating parameters of each box include size, resolution, and pixel spacing.
main components
To understand how the screen works and its composition, let's take a look at the main components that play a key role in its design and assembly.
LED modulesare the foundation of any screen. These modules consist of many LEDs arranged in a matrix. Each LED is responsible for reproducing a specific color, which allows you to create bright, rich images.
Controller and processor. The controller is responsible for receiving and processing video signals, and the processor performs the complex calculations required to correctly display the image. They ensure synchronization of all module operations. High image quality can be maintained even if lighting conditions change. Allows you to manage content and adapt it to various tasks.
Power supply. Convert the input voltage to the voltage required for the LED to operate to ensure stable operation of the screen. Prevent overheating and component failure. It is important to choose a power supply with sufficient power reserves to ensure that the screen can operate stably even under maximum load.
Cables and connectors. The stability and reliability of equipment depend on the quality of cables and connectors. They must be moisture-proof and dustproof.
software. Programs used to set up and manage screens. An application for creating and editing content. The software automates performance scheduling and equipment status monitoring.
Therefore, LED screens are composed of many components. These elements work together to provide high image quality and reliable operation, making LED screens indispensable in a variety of applications from advertising to information displays.
The main types of LED displays
cluster screen
The pixels of the LED cluster screen are composed of multiple LEDs-3 - 10. Each cluster has its own connector for connecting and has a sealed design. Clusters are usually encapsulated in a shell. They are also equipped with a variety of supporting equipment-lenses, reflectors, sun visors. Cluster technology stems from the architecture of the first linear LED screens, in which one light is equivalent to a pixel, with a separate control panel.
matrix screen
A more modern type is the matrix display. In their design, the cluster is combined with a control board, and the operation of each pixel is regulated through an information bus.
Divided by LED installation method
DIP (In-Line Package)
The screen contains three basic colors of light bulb LED elements, mounted on the base (directly mounted cluster). The size of LEDs has some limitations on pixel spacing-rarely less than 7 millimeters. Such screens are mainly used outdoors. The DIP display is brighter, allowing you to play clear images in natural light.
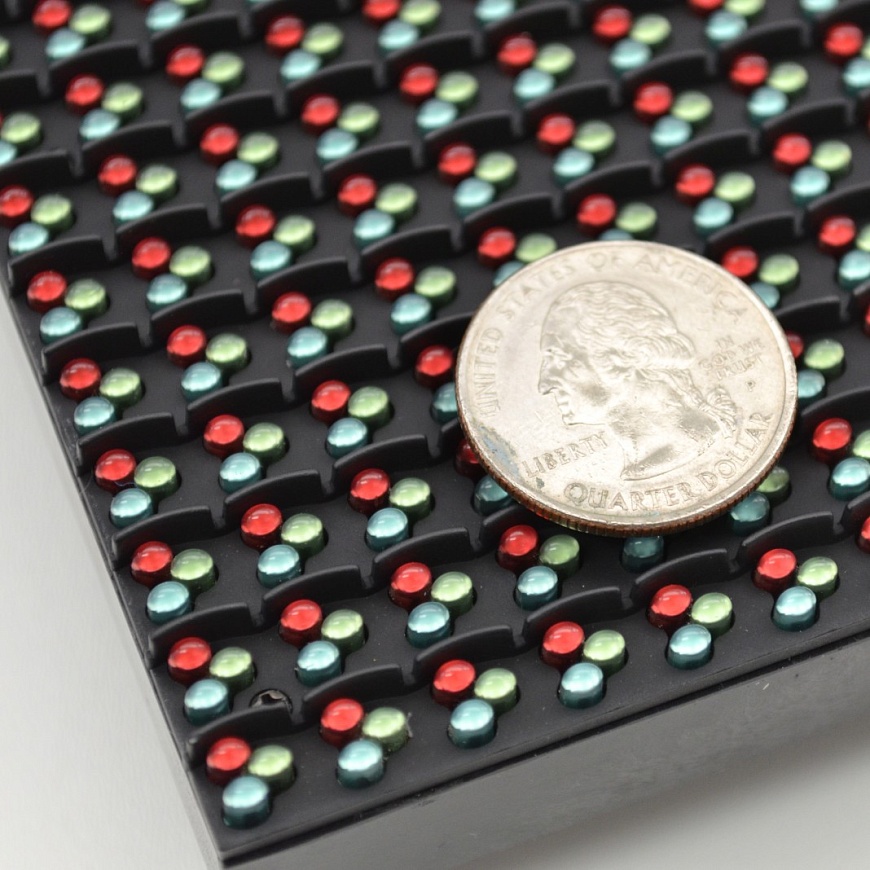
SMD (Surface Mount Device)
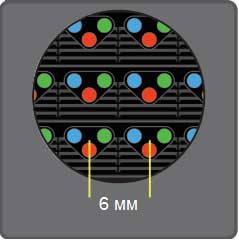
Surface mounting involves combining three color LEDs on one spot. They are very small-just a few millimeters-which makes them invisible. Due to the small pixel spacing (as low as 1.6 mm and less), this type of screen has very high resolution. SMD displays can be used indoors because the image remains clear even when viewed up close.
according to purpose
Internal and external LED screens. Indoor equipment is suitable for indoor use, and outdoor equipment is suitable for outdoor use. The outdoor model has a special climate design that protects the enclosure from moisture. They are highly resistant to temperature changes and direct sunlight.
Based on body structure
The housing structure of LED displays is also different.
The chassis modelis large and requires fasteners to install it.
Framelless modelsare attached to glass and shop windows using special glue. Under the influence of ultraviolet light, the glue hardens to ensure reliable fixation of the equipment. Framelless technology is used to broadcast advertisements or create interactive displays.
As technology advances, new methods have emerged to improve screen performance and durability: COB (chip on board) and GOB (glue on board). COB technology involves mounting LED chips directly onto a printed circuit board to better protect components from mechanical damage. GOB technology involves the application of a special transparent adhesive protective layer to protect LED screen modules from moisture and dust.
The main characteristics of LED display
When selecting a screen, consider its characteristics.
brightness
This parameter greatly affects the quality of broadcast images and their perception by viewers. This is especially important to consider for indoor models. The optimal brightness value of street model is about 8000 CD per square meter. For monitors operating indoors, this value is 2500 CDs per 1 m2.
Pixel pitch and viewing distance
When selecting an LED display, you need to consider the expected installation location and distance from the viewer. The formula for calculating the minimum viewing distance for an image to remain clear is: pixel spacing x 1500. The maximum viewing distance is calculated as: screen height x 20.
viewing angle
Viewing angle is a parameter that determines how far a user can view the screen without color, contrast, and brightness distortion. This parameter is particularly relevant to the screen. Screens are often used in environments that cannot be avoided from being seen from different directions: streets, public places, or large rooms.
The impact of perspective on image perception is significant. The wide viewing angle LED screen provides clear and bright images even when viewed from the side. As a result, the information or advertising reaches a larger audience.
Technologies that affect screen viewing angle:
LED size and shape: Smaller LEDs have more precise directions and can improve viewing angles.
Pixel configuration: The location and density of the LEDs affect how images are perceived from different angles.
Surface coating: A matte or anti-reflective coating helps reduce reflections and improve viewing angle.
LED screen control system
Data processing and transmission. Input signals are converted to digital form and transmitted over the network to each individual screen module. Achieve high display accuracy and minimize latency. Use special error correction algorithms.
Synchronization and calibration. Synchronization ensures that content on all modules is displayed simultaneously, which is important when managing screen networks. Calibration in turn ensures accurate matching of color and brightness, making the picture more realistic and pleasing to the eye.
Main stages of synchronization and calibration:
- Check and set time parameters
- Adjustment of brightness and color rendering
- Testing, display adjustment
Type of control system
Let's take a look at their characteristics and differences.
Internal screen system. Designed specifically for indoor use: conference rooms, shopping centers, offices. Output devices provide high resolution and brightness, allowing you to transmit clear, rich images. They can be connected to a computer, media player, or other signal source.
External screen system. The design takes into account the specific conditions of outdoor use. They must be able to withstand weather conditions such as rain, snow and solar radiation. Controller and signal amplifier ensure stable operation. It is also important to consider that such systems often require additional cooling to prevent components from overheating.
Advantages of LED display
- Long service life. The service life of displays often reaches 100,000 hours. But after 10 years of operation, the image brightness may drop to half of the original parameters;
- High flexibility. Modular technology allows you to assemble any structure from individual clusters without obvious seams or seams. Huge multimedia surfaces up to tens of meters in length and width can be assembled and obtained in different configurations. Custom designs are often used in advertising, video walls or information boards;
- Convenient installation and maintenance. LED equipment is very easy to install and connect. The completed structure can be used effectively and does not require special maintenance. The surface can be replenished with a new cabinet or replaced with damaged areas;
- High quality color rendering and high brightness. Unlike LCD technology, LEDs are independent light sources. Thanks to the high-quality LEDs and their arrangement of up to 6 per pixel, high image brightness and good visibility can be achieved even in daylight. The brightness can be adjusted for playback in the dark. Wide viewing angle (up to 140 degrees) ensures that video quality at different viewing points does not cause color distortion;
- Moving pictures. LED elements quickly process signals from the control unit, allowing you to quickly change parameters without video delay or picture distortion;
- Versatile. LED modules can be mounted on either a flat surface or a curved surface. Simple operating parameter settings allow you to convey various information to the audience in the required format, connect multiple storage media and control it remotely;
- High efficiency. Such advertising or information devices can allow you to stand out from your competitors and confidently attract the attention of potential customers. LED screens combine high reliability with effective content display.
Disadvantages of LED screens
These include limited viewing distances due to low resolutions and prominent individual pixels in large designs. When installing it on the roof of a building, you need to choose a model with a large pixel spacing, otherwise errors will cause the image to be unclear.
LEDs are a type of light source, so the equipment consumes a lot of energy while constantly running. For example, each 30x30 pixel SMD cabinet with a pitch of 1 cm consumes approximately 40 watts. A large screen-6x8 meters-will consume 6 kilowatts of electricity.
In addition, the production and installation of screens require a large budget. Outdoor advertising types are simpler, with less investment, but the effect is poor. There are currently no similar products for LED displays, so their advantages and efficiency will offset costs over time.
LED Screen-A Brief Overview of the Application
Here are some examples of their use:
- At events, conferences, exhibitions and participant booths.
- They are installed in shopping centers and stores to inform current promotions, events, products and supplier news.
- Play advertisements, information about driver and pedestrian directions, distances, speeds and other data on busy streets and highways.
- Can be used to display information about sports games to the audience: scores, recordings, time replays.
- Used to create attractive decorations in movie theaters that display additional information about the movie, such as trailer, cast and crew information, and upcoming show times.
- In the control room, situation monitoring and expert analysis center.
conclusion
Modern technology continues to develop.
TAG:
Guess you want to see it
Popular information
-
LED display: type, design characteristics, how to choose an LED display
-
Research on LED display devices: basic concepts
-
How to choose the right LED display for you? The subtlety lies in the details

-
Introduction to outdoor naked-eye 3Dled display knowledge

-
How to view DIP,MSD,GOB,COB and other LED display technologies
the charts
- Introduction to outdoor naked-eye 3Dled display knowledge
- Research on LED display devices: basic concepts
- LED display: type, design characteristics, how to choose an LED display
- How to view DIP,MSD,GOB,COB and other LED display technologies
- How to choose the right LED display for you? The subtlety lies in the details