How to view DIP,MSD,GOB,COB and other LED display technologies
- author:
- 2024-09-03 16:35:13
How to choose an LED display? What characteristics should I pay attention to? What is the difference between RGB and SMD LEDs? Which one suits me? What are real pixels and virtual pixels?
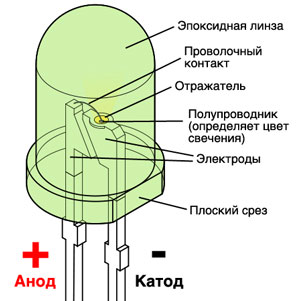
We will start with the device and working principle of LEDs.
The main component of an LED is a semiconductor, which emits light when current passes through it. It is surrounded by a reflector that directs light in the desired direction and is encapsulated in a transparent epoxy housing. Sometimes the housing is painted, but this is just for convenience so you can determine the color of the diodes without turning them on. In fact, the color of the diode is determined by the type of semiconductor crystal
Each crystal emits a strictly defined color. If the chemical composition of the crystal changes slightly, the range of light emitted changes.
It happens that the colors of LEDs from the same manufacturer and different batches are slightly different. If these LEDs fall into the same ice screen, they will be visually obvious.
In order to avoid such trouble, you need to buy screens from large manufacturers. They have the ability to order LEDs in large quantities and ensure that no different LEDs are installed on the same screen. Some even have their own LED production and carry out multi-level quality control.
In addition, the cost of diodes is also affected by the electrode materials (gold wire diodes are more durable than copper wire diodes).
It should also be noted that all-black diodes have appeared on the market. They have significantly higher contrast, but slightly lower brightness.
The LED responds immediately to turn on/off, so the LED screen does not have the cyclic effect observed in dynamic images of some LCD panels"". Their life cycle does not depend on the number of switches. Existing video screens (LCD, CRT, plasma, projection) cannot compete with LED screens in terms of contrast and viewing angle in the sun.
The service life of LEDs is usually specified as a maximum loss of 50% of brightness. This means that the screen will continue to work, but with lower brightness.
LED screens (or ice screens) are displays that use LEDs to form images.
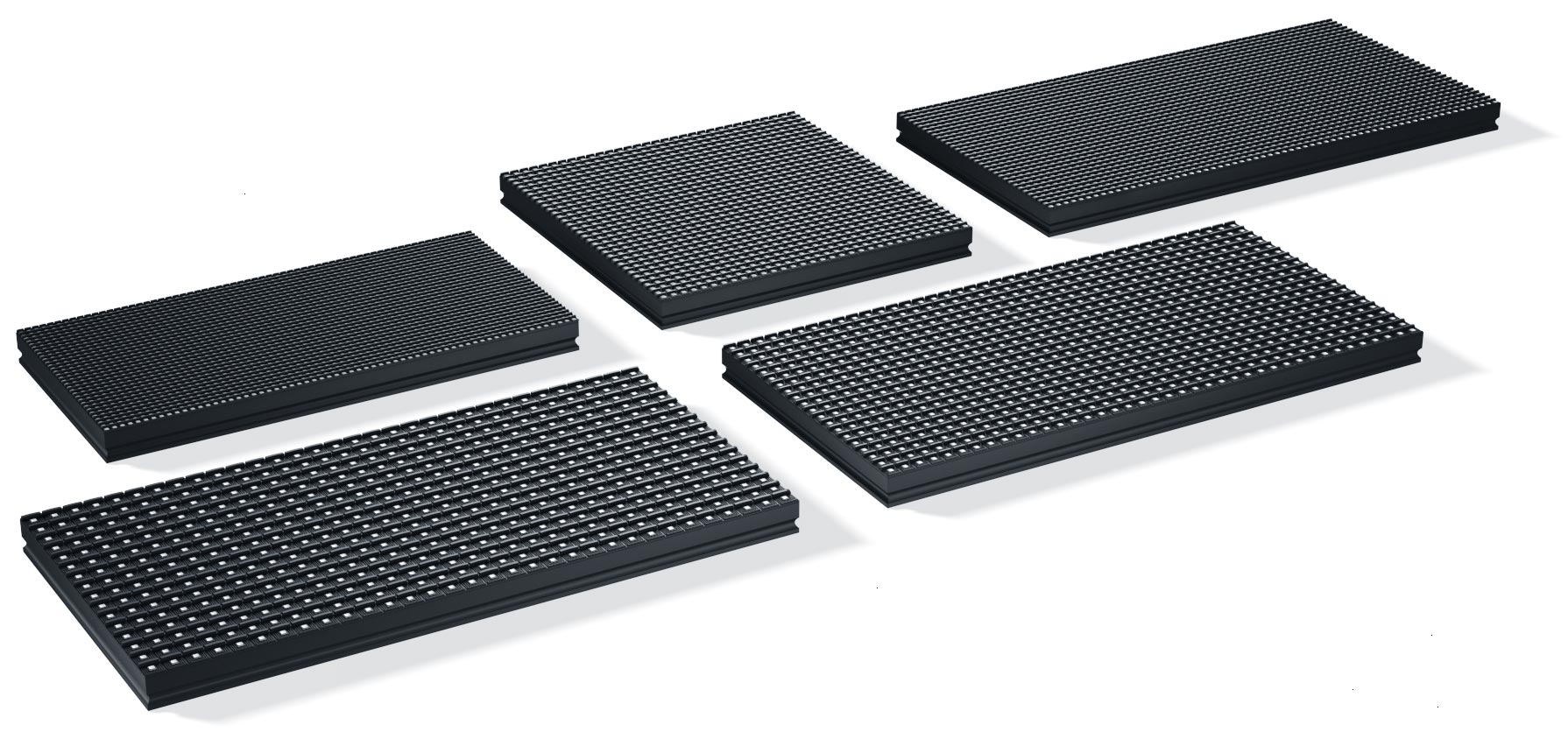 The LED panel or module is the component part of the assembly of the LED screen. All LED displays are produced in the form of standard modules and then assembled to the required size. The size of the module varies depending on the manufacturer and type of screen. Therefore, when ordering a screen, you need to be prepared, and the size may be slightly different from the required size. Of course, you can customize modules with non-standard size, but this will affect the price of the screen.
The LED panel or module is the component part of the assembly of the LED screen. All LED displays are produced in the form of standard modules and then assembled to the required size. The size of the module varies depending on the manufacturer and type of screen. Therefore, when ordering a screen, you need to be prepared, and the size may be slightly different from the required size. Of course, you can customize modules with non-standard size, but this will affect the price of the screen.
LED panels are sometimes also referred to as LCD panels with LED backlights. This is a misnomer because they only use LEDs to create the backlight and the image is formed by a liquid crystal display (LCD).
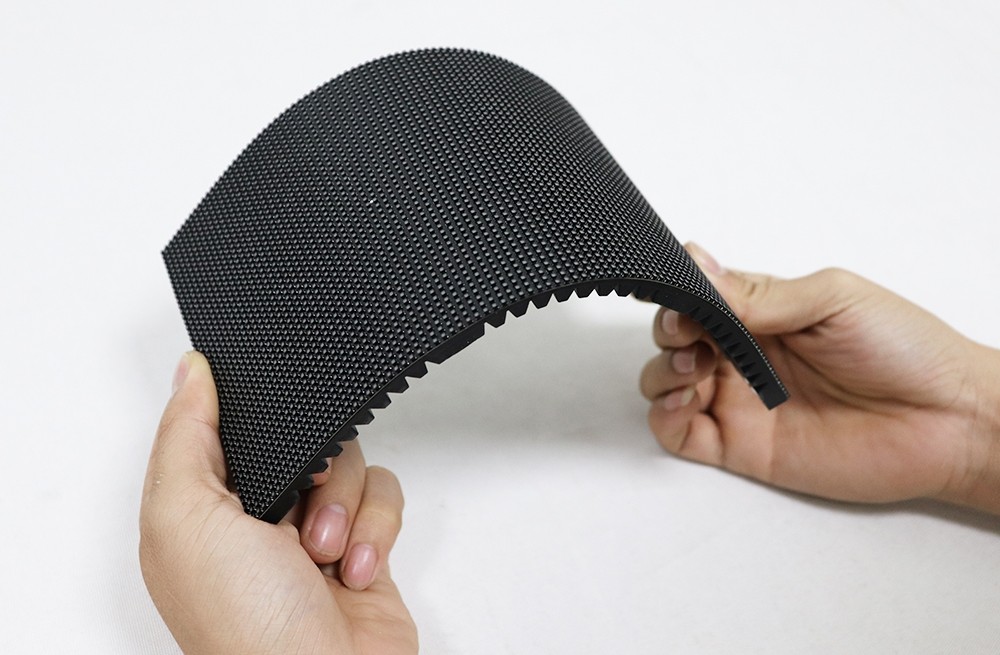
In addition to rigid modules, flexible modules with stable quality can now be used. Use them to assemble curved screens.

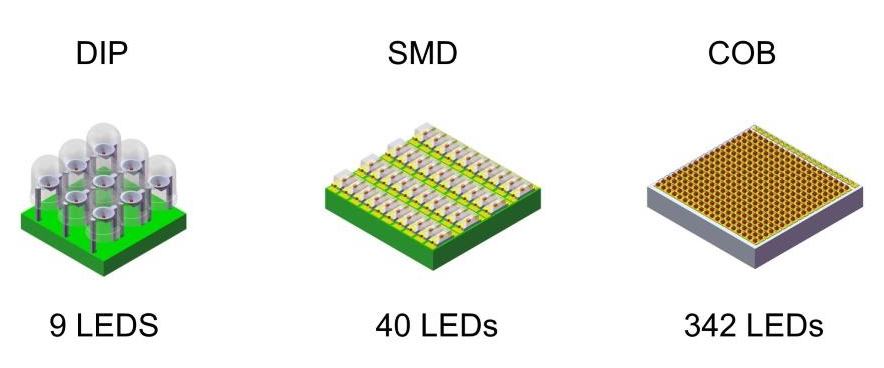
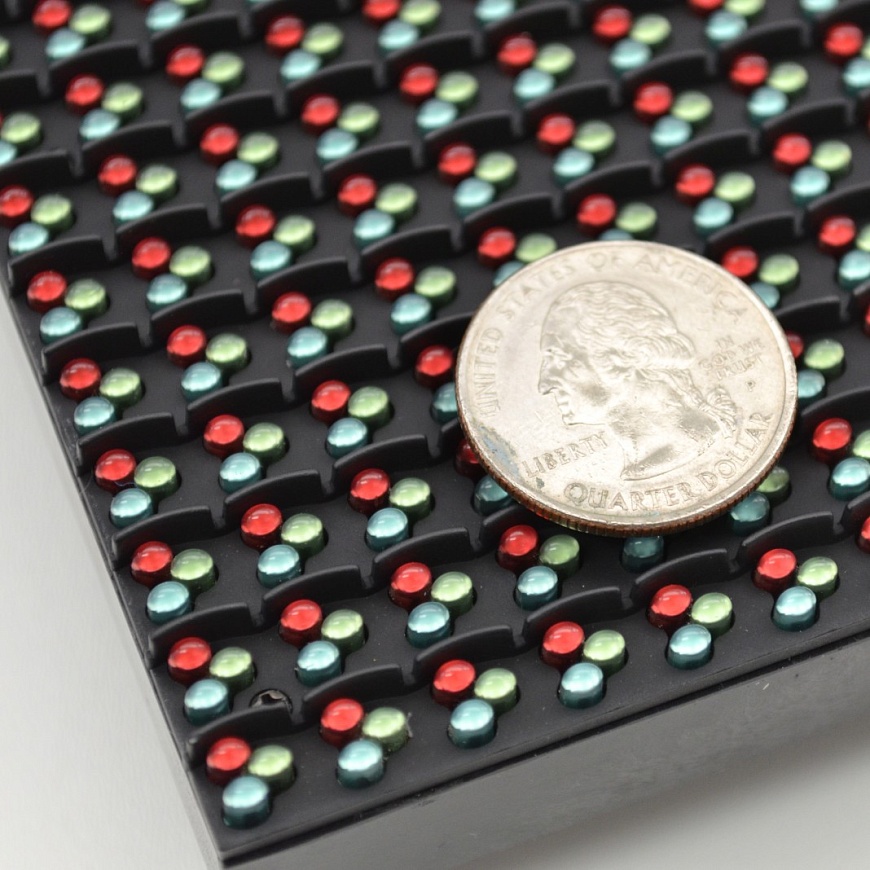
The difference between LED screens lies in the type of arrangement of LEDs on the board. At present, the main common types of ice screens are DIP and SMD.
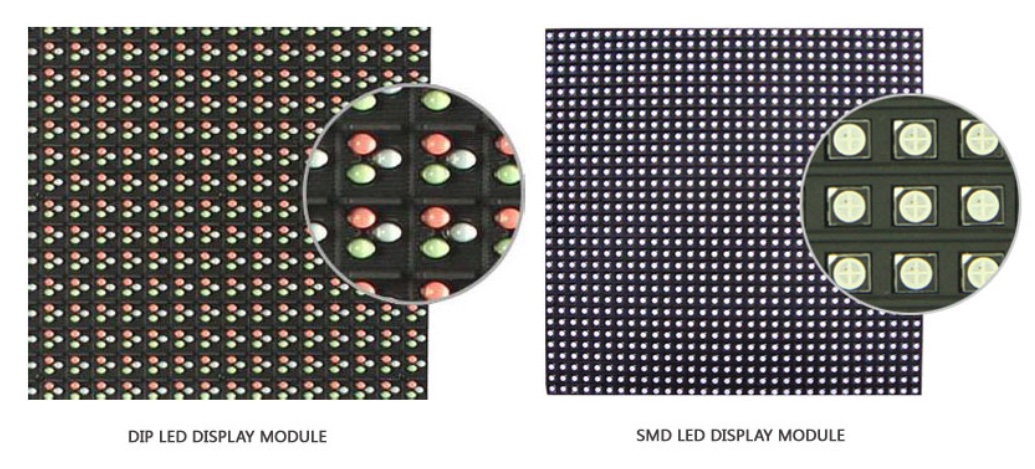
For the first type of screen, individual LEDs of different colors are combined into groups of several blocks. Each such group forms a pixel. There is at least one red, blue and green LED in a group. By mixing these three basic colors, you can get the entire spectrum. The screens made with RGB technology are brighter and are specially designed for outdoor use.
The second type of screen consists of SMD LEDs, in which semiconductors of different" colors" are sealed in a housing. Each LED is a pixel that reproduces the color of the entire spectrum. Visually, the second type of screen has a flatter and smoother surface. SMD screens have lower brightness but higher resolution. They can be used outdoors and indoors.
The third type is COB/GOB. It has only recently emerged and is designed for screens with very thin pixel spacing. This technology allows us to achieve higher pixel densities per unit area.
In this type of screen, the LEDs are grown directly on the board rather than soldered. At the top, the entire circuit board is filled with a transparent compound that protects electronic equipment from moisture and physical damage.
 The brightness of the LED screen is measured in units of nits (or cd/m ²).
The brightness of the LED screen is measured in units of nits (or cd/m ²).
For screens installed in corridors, 600 nits of brightness may be enough. Exhibitions, performances or concerts may require higher brightness. On the other hand, for a TV studio, you may need to reduce the brightness. The advantage of SMD screens is that when the brightness decreases, the color gamut remains unchanged.
For outdoor LED displays, the brightness should be at least 2000 nits. Ensure readability in direct sunlight-at least 5000 nits. Some DIP models have brightness up to 12,000 nits, which improves visibility at long distances-which is crucial if viewing the screen from a distance. In this case, the brighter the screen, the higher the audience coverage. Equally important, the ice curtain can automatically reduce brightness as dusk approaches.
LED screen resolution.
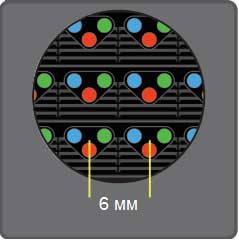
When talking about screen resolution, use the term" pixel spacing" (P3, P4, P6... P25)。
Pixel pitch is the distance between the centers of adjacent pixels (LED or SMD diode groups). The smaller the pixel spacing, the denser the LED arrangement, the higher the screen resolution, and the shorter the comfortable viewing distance. The pixel spacing is usually represented by the Latin letter P + a certain value. For example, P6 represents a screen with a pixel pitch of 6 mm. As of the time of writing, the minimum pixel spacing for LED screens is 1.6 mm, which allows you to achieve full HD resolution on screens that are only more than 3 meters wide. Serial screens have a maximum pixel spacing of 50 mm; used for translucent screens to create large media façades.
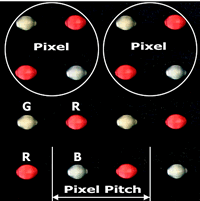
Pixel spacing or resolution is one of the most important characteristics when choosing an LED screen. It greatly affects cost and audience perception of the screen. Choosing the best pixel spacing is important to avoid paying exorbitant fees for pixels that no one sees, while providing the best image quality for viewers and advertisers.
What pixel spacing do you need? You can roughly estimate as follows. The pixel spacing is proportional to the comfortable viewing distance. In other words, screens with a spacing of 16mm (P16) are most comfortable to view at a distance of 16 meters. Starting at 10 meters, individual pixels can already be distinguished-the image will not be uniform, but will appear to be made up of points. Conversely, at a distance of 50 meters, you will not be able to distinguish small details, and such resolution is unnecessary. Therefore, to choose the best pixel spacing, you first need to evaluate the distance at which most viewers view the screen. If the distance is 25 meters or more (it makes no sense to pay too much for a 10 mm spacing), you need screens with a spacing of P25 or more.
Equipment maintenance is another important point to keep in mind when choosing the type of LED screen. LED
TAG:
Guess you want to see it
Popular information
-
How to choose the right LED display for you? The subtlety lies in the details

-
How to view DIP,MSD,GOB,COB and other LED display technologies
-
Introduction to outdoor naked-eye 3Dled display knowledge

-
LED display: type, design characteristics, how to choose an LED display
-
Research on LED display devices: basic concepts
the charts
- Introduction to outdoor naked-eye 3Dled display knowledge
- Research on LED display devices: basic concepts
- LED display: type, design characteristics, how to choose an LED display
- How to view DIP,MSD,GOB,COB and other LED display technologies
- How to choose the right LED display for you? The subtlety lies in the details