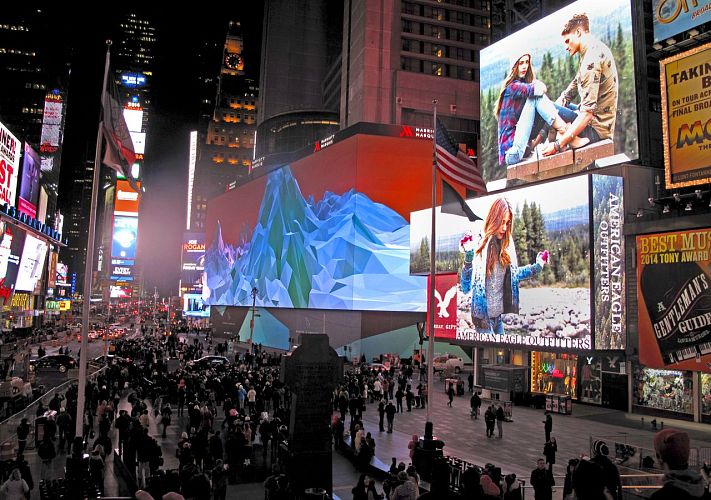
How to choose the right LED display for you? The subtlety lies in the details
- author: 德米特里·志林
- 2024-09-03 17:22:18

德米特里·志林/2024 年 1 月 28 日/
general definition
A light emitting diode screen (LED screen)is an information display device that forms an image from multiple semiconductor LEDs located on the surface of the screen. Each dot on the screen is a pixel and can contain one or more %20LEDs. Today, the LED%20 screen is one of the most promising visualization tools. This is why they are increasingly used as information boards, billboards, and even simply as creative decorative elements.
The first working prototype of an LED screen was exhibited at the EISEF Technology Exhibition in the United States on March 18, 1978. The author of the development,%20James%20Mitchell%20, said its main advantages were that it was simple image formation and low operating voltages compared to the popular %20CRT%20 displays at the time, which made it possible to use %20LED%20 screens in the future on portable devices driven by %20LED%20. A battery. Thanks to %20oled %20 technology (organic light emitting diodes), it was not until %2021%20th century that %20LED %20 was miniaturized to the size required to make traditional TVs.
LED%20 screens are not the first technology to produce moving images, but they are the first to provide such a wide range of functions. Contrasting full-color images during day and night, digital content, flexible display settings, and arbitrary screen geometries make the %20LED%20 screen a powerful tool for conveying important information to consumers and customers.
Working principle of LED screen
The LED%20 screen contains %20LEDs in three basic colors: red, green, blue %20(RGB)%20. A combination of these three colors of %20LED%20, working at different brightness, allows you to create any full-color image. This principle is similar to the principle of traditional TV or computer monitors.
The LEDs on the screen correspond to pixels, but unlike LCD screens, the pixels of the LED screen are virtual, that is, the pixels are virtual. LEDs of the same color can be part of multiple virtual pixels. This feature allows you to get twice the image resolution.
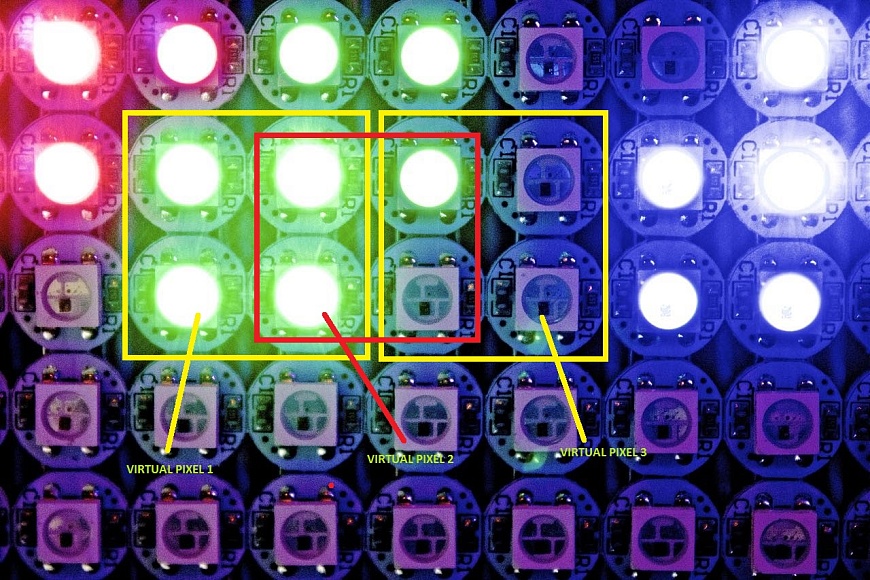
Design and classification of LED display
The LED display adopts modular design. LEDs are grouped into clusters or matrices and connected from the rear to control electronics. These individual modules (also called cabinets) operate independently, but they can be combined into a single structure in any configuration. As a result, traditional rectangular screens and screens with more complex shapes can be constructed-curved, convex, repeating the shape of their mounting surface. The key characteristics of the box are resolution, pixel spacing and size.
According to the design,LED displays are divided into two types:
- cluster
- matrix
Cluster screen
In a cluster screen, each pixel is a separate element, containing several LEDs (from three to dozens). The cluster is completely sealed and equipped with connectors for connection. The cluster can be enclosed in an enclosure and can also be equipped with additional equipment: lenses, reflectors, awnings, etc.
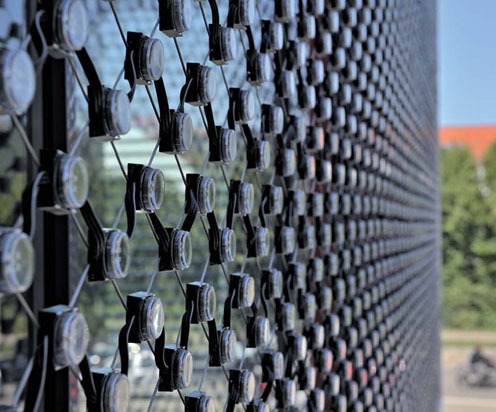


Historically, clustering technology first emerged as the logical development of the first LED screens, which consisted of lights with a linear architecture, in which one pixel was a light and also a control panel.
Among them, one image pixel is formed of four light-emitting elements (red, blue and two green) and connected to the control board to form a complete structure. Then connect this design to the module controller. With the development of LED technology, it has become possible to place all the LEDs of a pixel on a single semiconductor substrate using a single control electronics, so that you don't have to fiddle with each LED and just need to combine the cluster with the control board. Currently, cluster LED screens are considered obsolete, but they still have areas of application because... from an operational perspective, they are no worse than matrices.
matrix screen
Matrix screen technology is more advanced. Among them, the cluster itself and the control board are one unit, with individual pixels turning on/off through the information bus connected to each module.
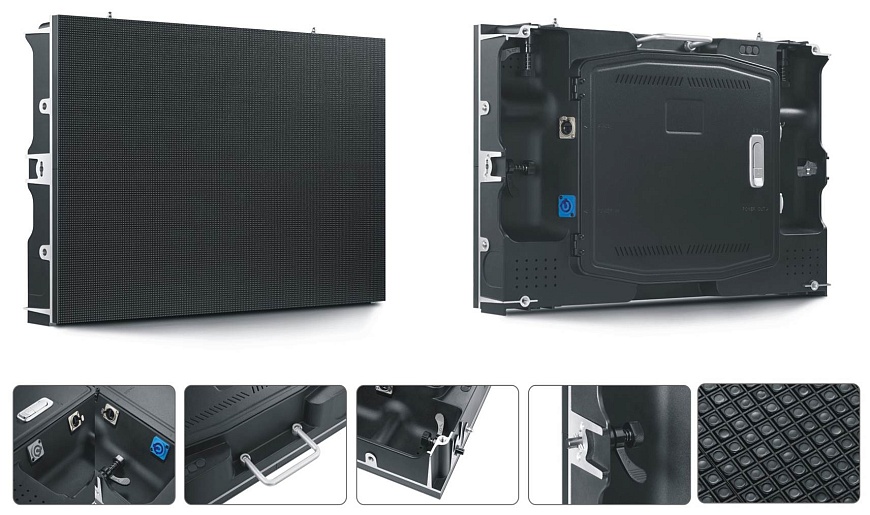

Depending on how the LEDs are placed, screens are divided into DIP and SMD screens-in-line package clusters and surface mount devices respectively.
DIP screen
In the DIP screen, three colors of traditional light bulb LEDs are mounted directly on the base. Due to the size of the bulb's LED, the pixel spacing of the DIP screen is rarely less than 7 mm. As a result, this type of LED screen is more often used outdoors and has the appropriate climate design of the device housing. In addition, the DIP screen has a high brightness, which also determines its use in bright natural light.
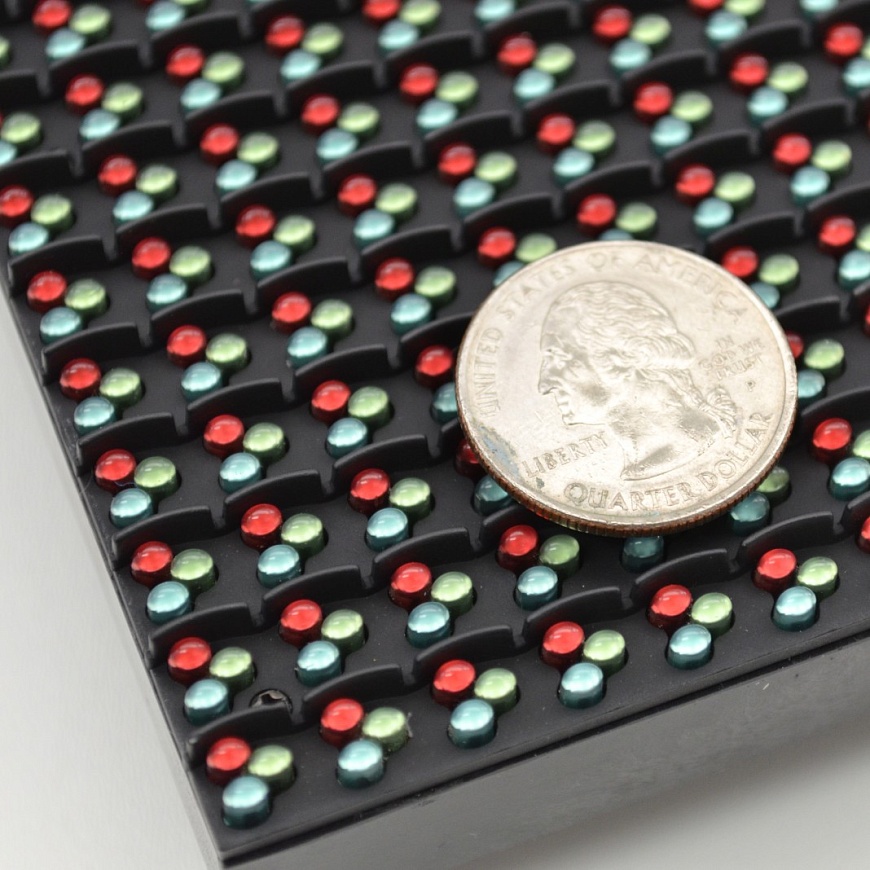

SMD screen
In SMD screens, R, G and B-LEDs are gathered at one point on the substrate. At the same time, the physical size of LEDs does not exceed a few millimeters, which means that even at a relatively close distance, they are no longer visible to the naked eye. The pixel spacing of SMD screens can reach a value of 1.6 mm or less, which means that the resolution of such screens is significantly higher than that of DIP. As a result, SMD technology is more commonly used for indoor screens.
According to its design, LED screens are divided into:
- Interior, suitable for indoor use
- Exterior, suitable for outdoor use.
The outdoor screen is designed and manufactured in a closed climate, has a waterproof shell, and is resistant to high temperatures and sunlight.
Depending on whether there is a shell,LED displays can be divided into framed screens and frameless screens. In the first case, the screen size is large and requires a special structure for installation. For example, frameless screens are bonded to the interior surface of shop window glass or walls using special glue that hardens under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. This technology makes it possible to obtain transparent display cases that can play advertising videos or interactive materials.
Selection of LED display
When selecting an LED display, you should pay attention to several parameters:
brightness

The brightness of the LED directly affects the perception of information on the LED screen, especially for screens installed outdoors. The optimal brightness for outdoor screens is considered to be 8000 candelas per square meter; for screens installed indoors, 2500 candelas per square meter is enough.
Please note that the rating of luminous flux power may differ from the actual value. Therefore, you should not pursue the cheapness of China LED screens without first ensuring that they do have the claimed characteristics, which unfortunately is not always the case.
optimal viewing distance
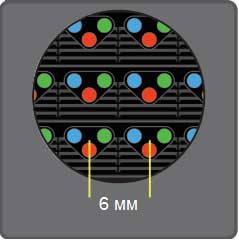
As mentioned above, large pixel spacing is not necessarily a disadvantage. It all depends on the viewing distance. A simple approximate formula for calculating the minimum observation distance is also given above:
Pixel spacing = minimum observation distance x 1.5
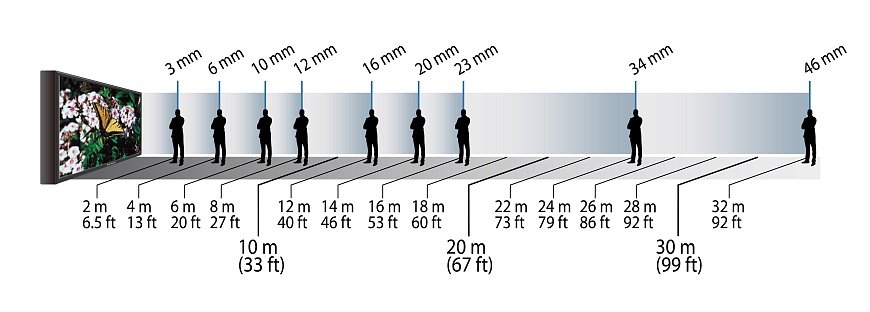
Therefore, for a screen with a pixel size of 3 millimeters, the minimum distance at which an image appears smooth is about 4.5 meters. Conversely, if you know the viewing distance, you can use a formula to determine the required pixel size for the LED screen.
pixel pitch
Based on the maximum viewing distance, you can determine the desired screen size. The maximum viewing distance is defined as twenty times the screen height, namely:
Maximum viewing distance = screen height *20
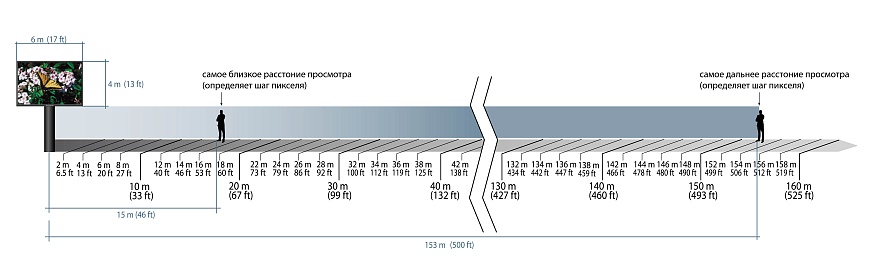
Therefore, if you want to clearly read the image on the LED screen at a distance of 150 meters, the vertical size of the screen should be at least 5-8 meters. The horizontal size can then be easily calculated based on the desired aspect ratio (4:3 or 16:9).
fault tolerance
An important parameter determines not only the useful life of the media facade, but also its ability to resist various types of external influences. High-quality screen manufacturers only use high-quality components: high-quality Nichia LEDs provide excellent color rendering, all high-quality screens have redundant configurations for equipment fault tolerance, and the exclusive use of EGI steel housings helps increase the service life of the equipment, and more. Therefore, when selecting an LED display, you must check it clearly, and it is best to trust professionals.
Advantages of LED display
- DurabilityModern LED displays have a service life of up to 100,000 hours. However, it is worth noting that during the service life of the LED, its brightness will gradually decrease, and after 10 years or more of use, the brightness will drop to 50% of the original brightness.
- Themodular design of the modular LED screen allows you to arrange the LED clusters as you wish, with no seams or visible seams. Screen size can reach tens of meters, and arbitrary configuration of modules allows the use of unusual design solutions and non-standard forms of information boards, video walls or billboards.
- Easy to install and maintainLED displays are characterized by simple installation and switching. The screen can expand very quickly if needed. At the same time, LED screens require little maintenance. The integrated design of the LED module is resistant to external influences. If needed, the light panels can be expanded by installing additional cabinets. Replacing faulty modules is also easy.
- Bright picture and perfect color reproductionDifferent from LCD screens built based on translucent technology of liquid crystal substrates and LED lighting of liquid crystal matrices, the LEDs of the LED screen themselves emit light. Thanks to modern ultra-bright diodes and arrangements of up to 6 diodes per pixel, today's LED screens exhibit excellent image brightness, allowing the information to be read perfectly even on bright days. Also worth noting is the ability to adjust LED brightness, as maximum brightness is not required at night. The viewing angle of the LED screen reaches 140 degrees, and the picture at extreme viewing angles will not fade or distort color. Extremely high contrast provides excellent image quality.
- Oneof the characteristics of high-dynamic LED technology is that it has no inertia at all. The LED processes the control signal with minimal delay and immediately changes its brightness. As a result, even the most dynamic video can be reproduced perfectly on such screens without lags, loops and artifacts.
- FlexibleLED modules can be mounted not only on flat surfaces, but also on curved surfaces. But in addition to design flexibility, the LED screen is also highly customizable, allowing you to play content from a variety of media. Screen configuration is done programmatically and is usually done remotely.
- Effect and efficiencyNo matter how you look at it, the LED screen looks amazing. Bright, dynamic images on the screen can convey to consumers absolutely arbitrary information that the customer chooses. At the same time, the content is even more eye-catching in the context of traditional billboards and logos; it attracts customers 'attention faster and more firmly, essentially combining the advantages of television or media advertising with the simplicity and reliability of traditional billboards. By correctly selecting the format and content of the content displayed on the LED screen, the latter will not only be amazing, but will also become an extremely effective tool for conveying information.
Disadvantages of LED screens
However, LED screens have some shortcomings that need to be considered:
- The resolution is relatively lowbecause the spacing between the LEDs is large (an average of 10 mm), so the LED screen cannot have high resolution. Therefore, the information on them must be read from a certain minimum distance so that individual pixels on the screen cannot be distinguished. This distance can be determined approximately by multiplying the standard pixel spacing by 1000. That is, for a screen with a pixel spacing of 10mm, the minimum viewing distance is 10m; for a screen with a spacing of 25 mm, this distance will already be 25 m, etc. So, I learned about LEDs
TAG:
Guess you want to see it
Popular information
-
How to view DIP,MSD,GOB,COB and other LED display technologies
-
How to choose the right LED display for you? The subtlety lies in the details

-
LED display: type, design characteristics, how to choose an LED display
-
Research on LED display devices: basic concepts
-
Introduction to outdoor naked-eye 3Dled display knowledge

the charts
- Introduction to outdoor naked-eye 3Dled display knowledge
- Research on LED display devices: basic concepts
- LED display: type, design characteristics, how to choose an LED display
- How to view DIP,MSD,GOB,COB and other LED display technologies
- How to choose the right LED display for you? The subtlety lies in the details
